- What is Geotextile Material?
- Main Types of Geotextile Materials and Their Characteristics
- Geotextile Material Price Reference and Budgeting Guide
- Functions of Geotextile Fabric
- Practical Application Scenarios for Geotextile Materials
- How to Select and Install Geotextile Material?
- Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)about Geotextile Material
- Conclusion
When a newly built road subsides prematurely or a garden drainage system consistently fails,the problem is often that you haven’t used a remarkable synthetic material—Geotextile Fabric Material.As the”versatile cloth”of modern civil engineering,geotextile material silently enhances the stability and durability of various projects through its four core functions:separation,reinforcement,drainage,and filtration.This guide provides a comprehensive overview of geotextile materials,including basic concepts,types,a price list,applications,and selection criteria.
What is Geotextile Material?
A geotextile is a permeable textile synthetic material used in geotechnical engineering.It is primarily manufactured from polymers like polypropylene(PP)or polyester(PET)through processes such as needle-punching,weaving,or heat-bonding.This type of geosynthetic material offers exceptional durability,resistance to chemical and biological degradation,and permeability,making it an indispensable foundation material in construction.

Main Types of Geotextile Materials and Their Characteristics
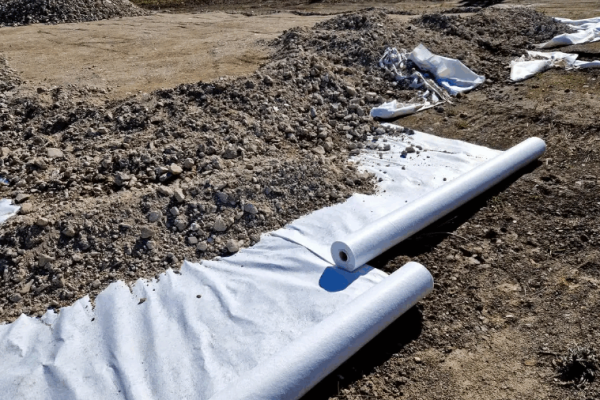
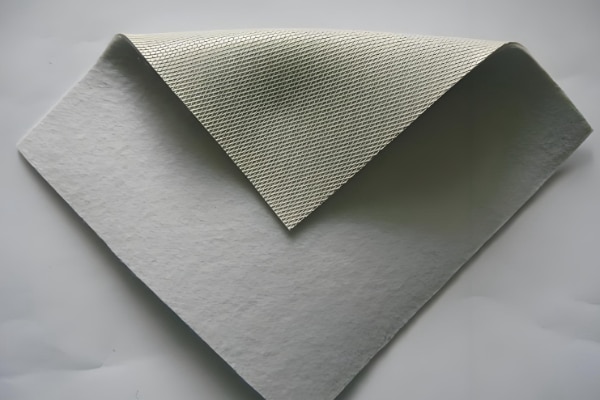
Nonwoven Geotextile
Manufacturing Process:Synthetic fibers are randomly arranged and bonded by mechanical needle-punching(the primary method),heat,or chemicals.
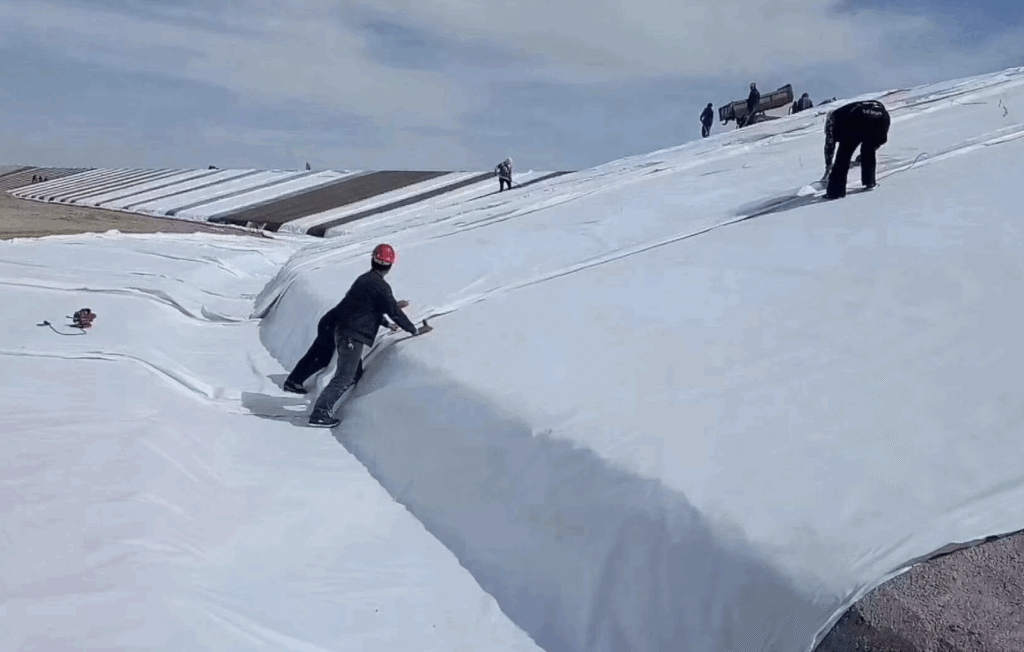
Characteristics:This nonwoven geotextile has a felt-like,fluffy appearance.It is isotropic and offers excellent elongation and in-plane water flow capacity.It is primarily used for filtration and drainage.
Common Applications:Road base drainage systems,filtration layers for slope protection,landfill leachate collection,and protection layers for pond liners.
Woven Geotextile Material
Manufacturing Process:Monofilament or multifilament yarns are interlaced in a regular pattern on a loom.
Characteristics:This woven geotextile resembles sacking material.It has high tensile strength and modulus but generally lower permeability.Its main uses are reinforcement and separation.
Common Applications:Reinforcement and separation for roads and railway bases,parking lots,reinforced soil walls,and land reclamation.
Nonwoven vs.Woven:How to Choose?
| Feature | Nonwoven Geotextile | Woven Geotextile |
| Manufacturing Process | Randomly oriented fibers, needle-punched | Yarns woven in a regular pattern |
| Appearance | Felt-like, fluffy | Sack-like, structured |
| Primary Function | Filtration, Drainage | Reinforcement, Separation |
| Permeability | High (water flow in all directions) | Moderate (depends on weave openings) |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate, high elongation | High, low elongation |
| Typical Applications | Drainage ditches, slopes, ponds | Road stabilization, foundations, parking areas |
Selection Principle:Choose nonwoven geotextile for drainage/filtration;choose woven geotextile material for high-strength reinforcement/separation.

Geotextile Material Price Reference and Budgeting Guide
Key Factors Influencing Geotextile Prices
Raw Material Costs:Prices for polymers like polypropylene fluctuate with the oil market.
Type and Manufacturing Process:The production of woven geotextile fabric is more complex,typically making it more expensive per unit than comparable nonwoven geotextile.
Technical Specifications:Weight(mass per unit area)and strength are the primary pricing factors.Higher parameters lead to higher prices.
Purchase Quantity:Buying full rolls(often hundreds of square meters)is cheaper per unit than buying cut pieces.
Brand and Certifications:Well-known brands or products with international certifications command a price premium.
If you are purchasing Geotextile Material, you can contact us!
Geotextile Material Market Price List(Example)
Important Note:The following prices are approximate market benchmarks in Chinese Yuan(CNY).Actual costs vary by region,supplier,order volume,and timing.Always request a current quote.
| Product Type | Specification (Weight, g/m²) | Primary Use | Approx. Price Range (USD/m²)) | Notes |
| Nonwoven Geotextile | 100 | Lightweight drainage, landscaping | 0.10 – 0.20 | Common for residential gardens |
| 200 | Standard road base, pond lining | 0.20 – 0.35 | Most common medium-duty grade | |
| 300 | Heavy-duty roads, parking areas, dams | 0.35 – 0.55 | High-strength requirements | |
| 400+ | Landfills, major civil works | 0.55+ | Custom specifications | |
| Woven Geotextile | 120 | Light reinforcement, soil stabilization | 0.25 – 0.40 | |
| 150 | Road separation, railway subgrade | 0.35 – 0.55 | ||
| 200+ | Heavy foundation, port projects | 0.55+ | High tensile strength |

How to Get Accurate Quotes and Control Costs?
Define Needs Clearly:Provide suppliers with specific project requirements and technical parameters(e.g.,”I need a 200g nonwoven geotextile with a CBR puncture strength of 3 kN”).
Request Samples:Ask for physical samples to check quality,thickness,and texture.
Compare Comprehensive Quotes:Evaluate the total price,including taxes and shipping,not just the unit product cost.
Tips for DIY Users:For small projects,check local building supply stores or online platforms,and inquire about purchasing cut pieces.
Functions of Geotextile Fabric
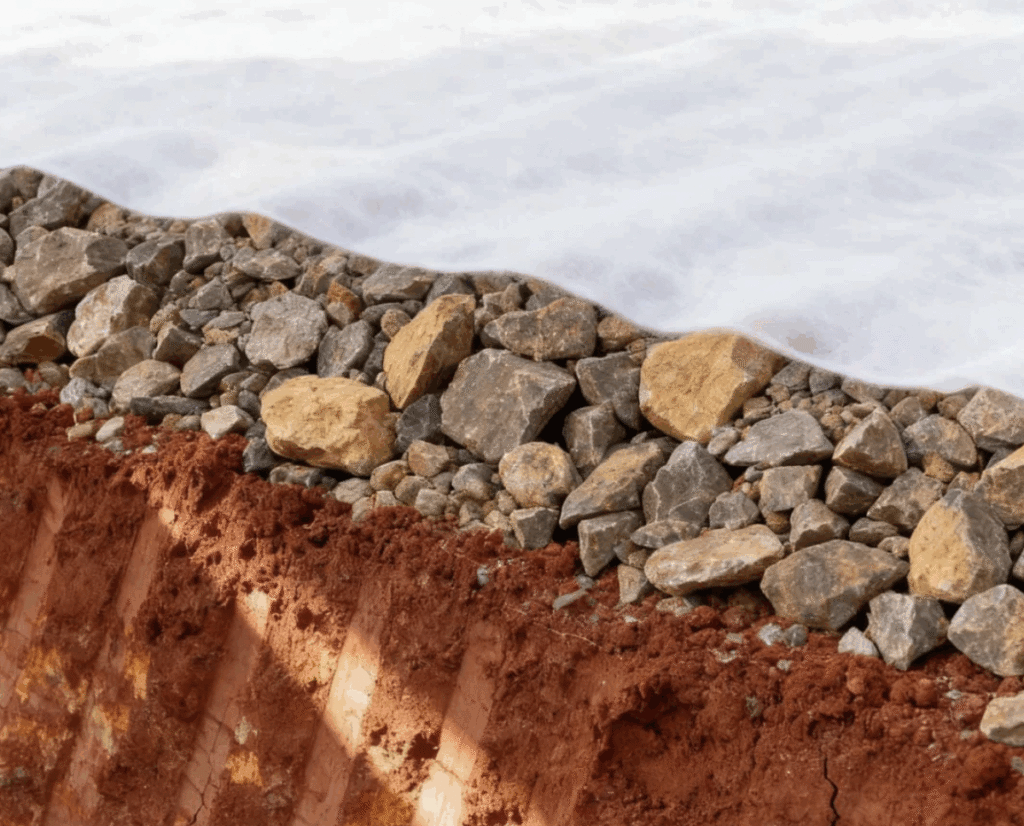
Separation:Placing geotextile material between dissimilar materials(e.g.,gravel and soft soil)prevents them from mixing,preserving the integrity and function of each layer.This saves material and maintains design thickness.
Reinforcement:The high tensile strength of the geotextile fabric,combined with soil friction,distributes loads and improves the stability and bearing capacity of soil masses,commonly used for reinforcing slopes and weak foundations.
Drainage:The permeable nature of geotextiles allows water to flow within their plane,effectively collecting and discharging it,thereby reducing water pressure.
Filtration:Acting as a stable filter,geotextile fabric permits water to pass while retaining soil particles,preventing erosion and ensuring the functionality of drainage systems.

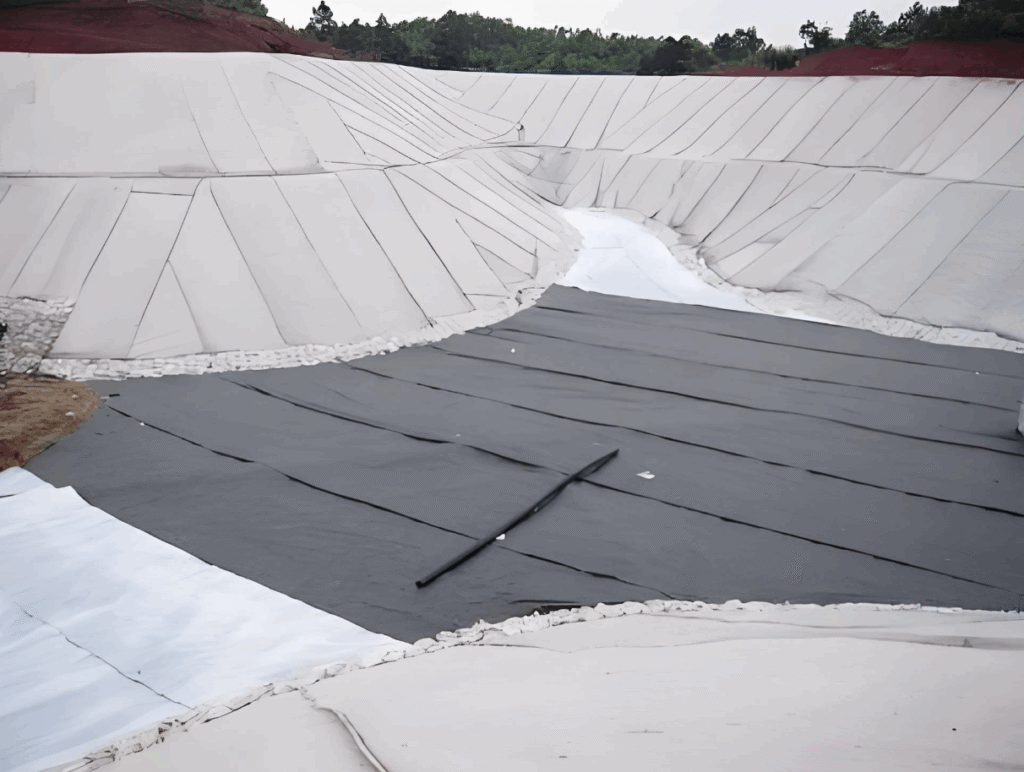
Practical Application Scenarios for Geotextile Materials
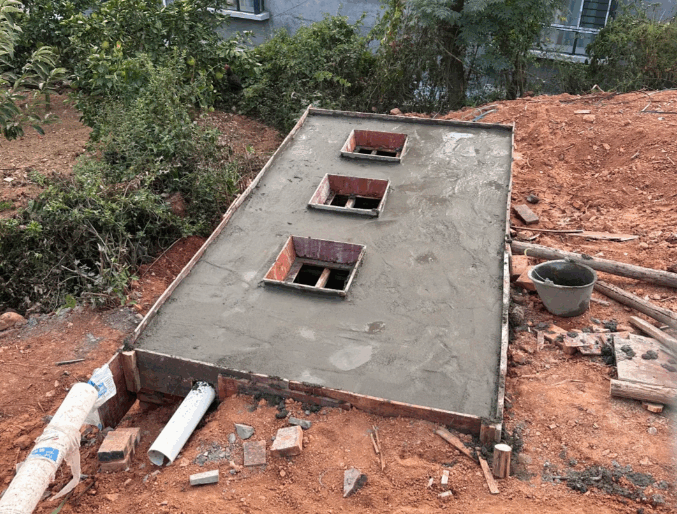
Roads and Railways:Used as a separation layer beneath the base course to prevent intermixing and provide drainage,significantly extending service life.
Drainage Systems:Wrapped around drainage pipes or stone aggregates to filter out soil particles and prevent clogging.
Erosion Control and Slope Reinforcement:Used with materials like geogrids to enhance stability;applied in riverbank protection.
DIY and Residential Projects:
Driveway Construction:Installing a woven geotextile on a compacted subgrade before adding gravel prevents rutting and deformation.
Yard Drainage:Creating a French drain using nonwoven geotextile fabric to wrap gravel solves waterlogging issues.
Garden Paths:Laying geotextile before placing pavers suppresses weed growth and stabilizes the base.
How to Select and Install Geotextile Material?
5 Key Parameters for Selecting Geotextiles
Weight per Unit Area(g/m²):Indicates thickness and density.Note:Higher weight correlates with durability but not necessarily tensile strength.
Tensile Strength(kN/m):The core indicator of resistance to pulling forces,critical for reinforcement.
Permeability Coefficient(cm/s):Indicates water flow capacity.Drainage applications require nonwoven geotextiles with high permeability.
Equivalent Opening Size(O90)(mm):Defines the ability to retain soil particles while allowing water passage.
CBR Puncture Resistance(kN):Measures resistance to penetration from sharp objects.
Key Steps for Geotextile Installation
Subgrade Preparation:Level and compact the area,removing debris like roots and sharp stones.
Placement Direction:Unroll the geotextile with the high-strength direction aligned with the primary stress.
Overlap Seams:Adjacent rolls should overlap by 30-50 cm.Sewing or specialized connectors are recommended for critical projects.
Temporary Anchoring:Use U-pins or sandbags for anchorage on slopes or in windy conditions.
Immediate Backfilling:Backfill immediately after installation to avoid UV degradation.Place backfill material carefully to avoid damage.

Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)about Geotextile Material
Q1:What is the difference between geotextile and geomembrane?
A:The fundamental difference is permeability.Geotextile fabric is permeable and used for drainage and filtration.A geomembrane(e.g.,HDPE liner)is impermeable and used for containment(e.g.,ponds,landfill liners).They are often used together,with the geotextile protecting the geomembrane from puncture.
Q2:What is the service life of geotextile material?
A:When properly designed and buried,polypropylene/polyester geotextiles are chemically stable and can have a design life exceeding 50 years.However,prolonged exposure to ultraviolet(UV)radiation accelerates aging,so it should be covered promptly.
Q3:Can I use regular canvas or landscape fabric instead of geotextile?
A:It is strongly discouraged.Canvas is impermeable and biodegradable.Cheap plastic landscape fabric degrades quickly and is easily punctured.Geotextile materials are engineered for specific performance and longevity.
Q4:Is a more expensive geotextile always better?
A:Not necessarily.The principle is fitness for purpose.Over-specifying leads to wasted budget.Select the most cost-effective product that meets your project’s specific design requirements with an adequate safety margin.
Conclusion
Although seemingly simple,geotextile material is a vital component underpinning the safety and durability of modern infrastructure.This guide has provided knowledge of its core functions,types,applications,and selection process.Whether for a large-scale project or a home garden upgrade,the correct use of geotextile fabric will ensure a more stable and long-lasting result.We hope this guide serves as a practical tool for your next project.
If you are looking for a reliable Geotextile Material supplier,please feel free to contact us.
About Us:Lianjie
Lianjie is a one-stop supplier of geosynthetics with 15 years of professional experience and multiple national certifications.We provide the most professional Geotextile Material solutions!
Reference Sources
ASTM International (American Society for Testing and Materials)
- ASTM D4439: Standard Terminology for Geosynthetics. This is the foundation for understanding all professional terminology related to geotextiles, geogrids, and related materials.
- ASTM D5261: Standard Test Method for Measuring Mass per Unit Area of Geotextiles (i.e., weight).
- ASTM D4632: Standard Test Method for Grab Breaking Force and Elongation of Geotextiles (a method for measuring tensile strength).
- ASTM D4751: Standard Test Method for Determining Apparent Opening Size (AOS) of a Geotextile (i.e., Equivalent Opening Size O95).
- ASTM D6241: Standard Test Method for Static Puncture Strength of Geotextiles and Geotextile-Related Products Using a 50-mm Probe (CBR Punch) (i.e., CBR Puncture Resistance).
ISO (International Organization for Standardization)
- ISO 10318: Geosynthetics – Terms and definitions.
- ISO 9863: Geosynthetics – Determination of thickness at specified pressures.